Sunscreen and Suncare Tips

We all love a bit of sunshine - whether enjoying a relaxing day at the beach, an afternoon stroll, or simply soaking up the sun’s rays with friends. While the sun is a source of warmth and happiness, it also speeds up our skin’s aging process and increases our risk of sun damage and developing skin cancer.
Thankfully, with the proper suncare routine, you can enjoy your time in the sun while helping to protect your skin and health.
This guide will cover all the essential sun safety tips, from how sunscreen works to the best ways to protect your skin from harmful rays all year round.
Bioré® Skincare is dedicated to helping you live life to the fullest with its UV Aqua Rich SPF 30 and 50 sunscreen and weightless moisturizer to offer powerful protection from UV rays while disappearing into skin without clogging pores along the way. Stay safe and shine bright with the Bioré® UV Aqua Rich sunscreen collection here.
Why is Sunscreen Essential?
It is never too late to start protecting your skin from the sun!
Sunscreen is crucial for shielding your skin from harmful UV rays, which can cause immediate damage like sunburn and long-term effects such as skin cancer and premature aging.
The Ultraviolet (UV) index, a measurement of the sun’s UV radiation strength, is a helpful guide to understanding when protection is necessary. Even on cloudy days or during cooler months, a moderate or high UV index still requires sunscreen to prevent skin damage.
Consistently applying sunscreen ensures you protect your skin’s health and appearance. It helps prevent issues like hyperpigmentation, fine lines, and wrinkles and can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer.
Is Sunscreen Important in Winter?
Yes! Sunscreen is just as important to consider wearing in winter as it is in summer.
Many assume that cooler, cloudy weather and a low UV index mean no sunscreen is needed, but that’s far from true. UV radiation impacts your skin year-round, and winter months often see higher UVA rays, which contribute to skin aging, especially if your skin is left unprotected.
Even if you don’t feel the burn, the damage still happens. Make sunscreen a part of your daily skincare routine, regardless of season, to ensure consistent protection against harmful UV rays.
Understanding UVA and UVB Rays
UVA and UVB rays affect the skin in different ways.
UVB rays are the primary cause of sunburn, but both UVA and UVB rays can lead to skin cancer.
- UVA rays penetrate deeper, contributing to photo-aging, causing dark spots, and breaking down collagen.
- UVB rays tend to damage the skin's outer layer, leading to visible burns.
Choosing sunscreens that offer broad-spectrum protection to guard against both types of UV radiation is essential.
How to Choose the Right Sunscreen
When selecting sunscreen, look for products with broad-spectrum protection that will shield your skin from UVA and UVB rays.
The higher the Sun Protection Factor (SPF), the better the coverage – SPF 30 or above is recommended for everyday use.
Also, consider your skin type when choosing a formula. For example, oily skin might prefer a lightweight, non-comedogenic option, while those with dry skin might benefit from sunscreens with hydrating properties.
Learn more about which Bioré® UV Aqua Rich sunscreen is best for your face and skin here.
When and How to Apply Sunscreen
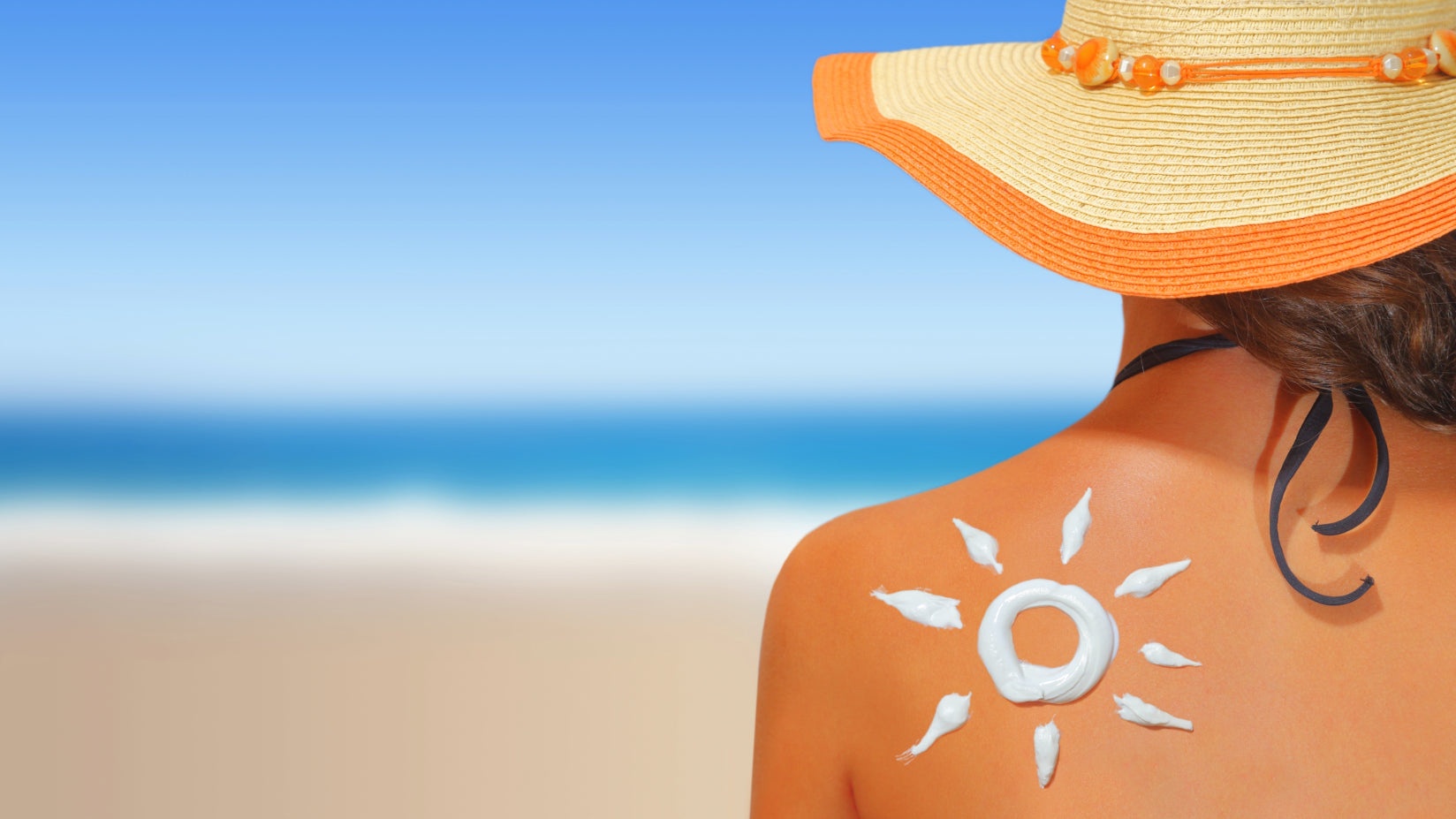
Apply sunscreen at least 20 minutes before sun exposure to allow it to absorb and create a protective barrier.
Use about one teaspoon for each area of your body, ensuring you don’t miss spots like your ears, neck, and the backs of your hands. Proper application is key to getting the maximum benefit from your sunscreen, so make sure you're using enough and reapplying as necessary.
It is essential to reapply sunscreen every two hours after swimming or sweating, even if your sunscreen claims to be water-resistant, as its efficacy will be limited after these activities.
Additional Sun Protection Measures
Sunscreen is only part of the solution when it comes to sun safety.
Here are some other ways to protect your skin from UV rays:
- Wear protective clothing:
- Seek shade:
- Protect your eyes:
These measures, combined with consistent sunscreen use, can drastically reduce your risk of sun damage and developing skin cancer.
Sunscreen for Different Skin Types
Different skin types can benefit from different sunscreen formulations.
If you have oily or acne-prone skin, look for non-comedogenic formulas that won’t clog pores.
Sensitive skin may benefit from mineral sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
Bioré® UV Aqua Rich is lightweight and non-greasy, meaning it won’t clog pores and is gentle on most skin types, including sensitive skin. Its moisturizing formula helps to hydrate dry skin, while its lightweight absorption is perfect for more oily complexions. Explore Bioré® UV Aqua Rich sunscreen to find the perfect fit to protect your skin.
Common Sunscreen Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, it’s easy to make errors when using sunscreen that can expose your skin to damage.
Here’s how to avoid some of the most common sunscreen pitfalls:
- Overlooking the label:
Not all sunscreens are created equal. Always choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect against both UVA and UVB rays. Opt for water-resistant formulas if you'll be swimming or sweating, and ensure it has an SPF of at least 30 for reliable protection.
- Not applying enough:
Many people use far less sunscreen than they should. You need about one ounce (roughly the size of a shot glass) to cover your entire body for full coverage. Make sure to apply it generously, including easy-to-miss areas like the ears, the back of the neck, and the tops of your feet.
- Skipping sunscreen on cloudy days:
Don’t be fooled by an overcast sky. Even on cloudy days, up to 80% of UV rays can still reach your skin. That’s why applying sunscreen daily, no matter the weather, is crucial for ongoing protection.
- Using outdated sunscreen:
- Relying on sunscreen alone:
Suncare for Children and Babies
Babies and young children have especially delicate skin that’s more vulnerable to sun damage. Early exposure to harmful UV rays significantly increases the risk of skin issues and even skin cancer later in life.
While sunscreen is an important tool for sun protection, it’s not always recommended for babies under six months due to their sensitive skin. Instead, other protective measures should be prioritized to keep them safe from the sun, such as:
- Cover up with clothing:
- Choose the right hat:
- Shade is essential:
- Time outdoor activities carefully:
- Use sunscreen for exposed skin:
The Importance of After-Sun Care
After a day in the sun, it’s essential to hydrate and soothe your skin. Not only will you feel better, but you can avoid the aging sun exposure side-effects from spending time in the sun like dehydration and damage,
Using a premium after-sun moisturizer with ingredients like aloe vera or vitamin B5 can help repair and calm the skin. Consistent after-sun care helps maintain skin health and can minimize the appearance of sun damage over time.
Natural and Mineral Sunscreens: Are They Effective?
Natural and mineral sunscreens contain ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide and offer effective protection by physically blocking UV rays.
These mineral-based filters sit on the skin’s surface and reflect sunlight, making them suitable for sensitive skin types and reducing the risk of irritation. However, mineral sunscreens can sometimes leave a white cast on the skin and may not blend as easily into the skin or with makeup.
Despite these limitations, natural sunscreens are less likely to cause allergic reactions than chemical sunscreens, so they are a great choice for those seeking gentle, effective sun defense.
Is Tinted Sunscreen any Different?
Tinted sunscreens can offer extra protection from blue light, which can contribute to the skin’s aging process.
According to a journal from Harvard Health, the iron oxides in tinted sunscreens can help reduce hyperpigmentation and prevent melasma relapses. Tinted sunscreens are also a great option for those looking for light coverage with added skin benefits.
Water-Resistant vs. Waterproof Sunscreen: What’s the Difference?
The term "waterproof" is misleading – no sunscreen is truly waterproof.
Instead, look for sunscreens labeled as “water-resistant,” which means they maintain their SPF protection for a certain period while you’re sweating or swimming. For example, a sunscreen that claims to be "4 hours water-resistant" will continue to offer the stated SPF level after being exposed to water for that duration, a claim that will have been rigorously lab tested.
Remember to reapply sunscreen after swimming or sweating to ensure continued protection.
Sunscreen and Vitamin D: Striking the Right Balance
Contrary to some beliefs, daily sunscreen use doesn’t cause vitamin D deficiency or stop your ability to tan.
Even high-SPF sunscreens allow a small amount of UV rays to reach the skin, enabling your body to produce enough vitamin D. Just 10 to 15 minutes of sun exposure a few times a week is typically sufficient. After that, it’s important to reapply sunscreen to protect against skin damage.
If you're concerned about vitamin D levels, you can supplement with vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy, or vitamin D supplements to maintain a healthy balance.
Does Sunscreen Expire?
Yes, sunscreen does expire and loses its effectiveness over time.
Always check the expiration date before using and replace any bottles past their prime. Most sunscreens have a shelf life of three years. Expired sunscreen won’t offer adequate protection, so it’s crucial to refresh your supply regularly.
Hot tip! If your sunscreen doesn’t have an expiration date, write the purchase date on the bottle to track its age.